1、Redis源码部署
yum install gcc -y #安装C依赖
tar zxvf redis-stable.tar.gz #解压
cd redis-stable
make PREFIX=/opt/app/redis install #指定目录编译
make install
mkdir /etc/redis #建立配置目录
cp redis.conf /etc/redis/6379.conf # 拷贝配置文件
cp utils/redis_init_script /etc/init.d/redis #拷贝init启动脚本针对6.X系统
chmod a+x /etc/init.d/redis #添加执行权限
修改配置文件:
vi /etc/redis/6379.conf
bind 0.0.0.0 #监听地址
maxmemory 4294967296 #限制最大内存(4G):
daemonize yes #后台运行
####启动与停止
/etc/init.d/redis start
/etc/init.d/redis stop
查看版本信息
#执行客户端工具
redis-cli
#输入命令info
127.0.0.1:6379> info
# Server
redis_version:4.0.10
redis_git_sha1:00000000
redis_git_dirty:0
redis_build_id:cf83e9c690dbed33
redis_mode:standalone
os:Linux 2.6.32-642.el6.x86_64 x86_64
arch_bits:64
multiplexing_api:epoll
golang操作redis
golang操作redis的客户端包有多个比如redigo、go-redis,github上Star最多的莫属redigo。
连接
Conn接口是与Redis协作的主要接口,可以使用Dial,DialWithTimeout或者NewConn函数来创建连接,当任务完成时,应用程序必须调用Close函数来完成操作。
get、set
_, err = c.Do("SET", "user_name", "luke")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("数据设置失败:", err)
}
username, err := redis.String(c.Do("GET", "user_name"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("数据获取失败:", err)
} else {
fmt.Println("2.1.获取user_name", username)
}
设置key过期时间
_, err = c.Do("SET", "user_name2", "luke", "EX", "5")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("数据设置失败:", err)
}
批量获取mget、批量设置mset
列表操作
package main
import (
"http://github.com/garyburd/redigo/redis"
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
conn,err := redis.Dial("tcp","10.1.210.69:6379")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("connect redis error :",err)
return
}
defer conn.Close()
_, err = conn.Do("LPUSH", "list1", "ele1","ele2","ele3")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("redis mset error:", err)
}
res, err := redis.String(conn.Do("LPOP", "list1"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("redis POP error:", err)
} else {
res_type := reflect.TypeOf(res)
fmt.Printf("res type : %s \n", res_type)
fmt.Printf("res : %s \n", res)
}
}
//res type : string
//res : ele3
hash操作
package main
import (
"http://github.com/garyburd/redigo/redis"
"fmt"
"reflect"
)
func main() {
conn,err := redis.Dial("tcp","10.1.210.69:6379")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("connect redis error :",err)
return
}
defer conn.Close()
_, err = conn.Do("HSET", "student","name", "wd","age",22)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("redis mset error:", err)
}
res, err := redis.Int64(conn.Do("HGET", "student","age"))
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("redis HGET error:", err)
} else {
res_type := reflect.TypeOf(res)
fmt.Printf("res type : %s \n", res_type)
fmt.Printf("res : %d \n", res)
}
}
//res type : int64
//res : 22
Pipelining(管道)
管道操作可以理解为并发操作,并通过Send(),Flush(),Receive()三个方法实现。客户端可以使用send()方法一次性向服务器发送一个或多个命令,命令发送完毕时,使用flush()方法将缓冲区的命令输入一次性发送到服务器,客户端再使用Receive()方法依次按照先进先出的顺序读取所有命令操作结果。
Send(commandName string, args ...interface{}) error
Flush() error
Receive() (reply interface{}, err error)
- Send:发送命令至缓冲区
- Flush:清空缓冲区,将命令一次性发送至服务器
- Recevie:依次读取服务器响应结果,当读取的命令未响应时,该操作会阻塞。
示例:
package main
import (
"http://github.com/garyburd/redigo/redis"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
conn,err := redis.Dial("tcp","10.1.210.69:6379")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("connect redis error :",err)
return
}
defer conn.Close()
conn.Send("HSET", "student","name", "wd","age","22")
conn.Send("HSET", "student","Score","100")
conn.Send("HGET", "student","age")
conn.Flush()
res1, err := conn.Receive()
fmt.Printf("Receive res1:%v \n", res1)
res2, err := conn.Receive()
fmt.Printf("Receive res2:%v\n",res2)
res3, err := conn.Receive()
fmt.Printf("Receive res3:%s\n",res3)
}
//Receive res1:0
//Receive res2:0
//Receive res3:22
发布/订阅
redis本身具有发布订阅的功能,其发布订阅功能通过命令SUBSCRIBE(订阅)/PUBLISH(发布)实现,并且发布订阅模式可以是多对多模式还可支持正则表达式,发布者可以向一个或多个频道发送消息,订阅者可订阅一个或者多个频道接受消息。
发布者:
订阅者:
操作示例,示例中将使用两个goroutine分别担任发布者和订阅者角色进行演示:
package main
import (
"http://github.com/garyburd/redigo/redis"
"fmt"
"time"
)
func Subs() { //订阅者
conn, err := redis.Dial("tcp", "10.1.210.69:6379")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("connect redis error :", err)
return
}
defer conn.Close()
psc := redis.PubSubConn{conn}
psc.Subscribe("channel1") //订阅channel1频道
for {
switch v := psc.Receive().(type) {
case redis.Message:
fmt.Printf("%s: message: %s\n", v.Channel, v.Data)
case redis.Subscription:
fmt.Printf("%s: %s %d\n", v.Channel, v.Kind, v.Count)
case error:
fmt.Println(v)
return
}
}
}
func Push(message string) { //发布者
conn, _ := redis.Dial("tcp", "10.1.210.69:6379")
_,err1 := conn.Do("PUBLISH", "channel1", message)
if err1 != nil {
fmt.Println("pub err: ", err1)
return
}
}
func main() {
go Subs()
go Push("this is wd")
time.Sleep(time.Second*3)
}
//channel1: subscribe 1
//channel1: message: this is wd
事务操作
MULTI, EXEC,DISCARD和WATCH是构成Redis事务的基础,当然我们使用go语言对redis进行事务操作的时候本质也是使用这些命令。
MULTI:开启事务
EXEC:执行事务
DISCARD:取消事务
WATCH:监视事务中的键变化,一旦有改变则取消事务。
示例:
连接池使用
redis连接池是通过pool结构体实现,以下是源码定义,相关参数说明已经备注:
type Pool struct {
// Dial is an application supplied function for creating and configuring a
// connection.
// The connection returned from Dial must not be in a special state
// (subscribed to pubsub channel, transaction started, ...).
Dial func() (Conn, error) //连接方法
// TestOnBorrow is an optional application supplied function for checking
// the health of an idle connection before the connection is used again by
// the application. Argument t is the time that the connection was returned
// to the pool. If the function returns an error, then the connection is
// closed.
TestOnBorrow func(c Conn, t time.Time) error
// Maximum number of idle connections in the pool.
MaxIdle int //最大的空闲连接数,即使没有redis连接时依然可以保持N个空闲的连接,而不被清除,随时处于待命状态
// Maximum number of connections allocated by the pool at a given time.
// When zero, there is no limit on the number of connections in the pool.
MaxActive int //最大的激活连接数,同时最多有N个连接
// Close connections after remaining idle for this duration. If the value
// is zero, then idle connections are not closed. Applications should set
// the timeout to a value less than the server's timeout.
IdleTimeout time.Duration //空闲连接等待时间,超过此时间后,空闲连接将被关闭
// If Wait is true and the pool is at the MaxActive limit, then Get() waits
// for a connection to be returned to the pool before returning.
Wait bool //当配置项为true并且MaxActive参数有限制时候,使用Get方法等待一个连接返回给连接池
// Close connections older than this duration. If the value is zero, then
// the pool does not close connections based on age.
MaxConnLifetime time.Duration
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
package main
import (
"http://github.com/garyburd/redigo/redis"
"fmt"
)
var Pool redis.Pool
func init() { //init 用于初始化一些参数,先于main执行
Pool = redis.Pool{
MaxIdle: 16,
MaxActive: 32,
IdleTimeout: 120,
Dial: func() (redis.Conn, error) {
return redis.Dial("tcp", "10.1.210.69:6379")
},
}
}
func main() {
conn :=Pool.Get()
res,err := conn.Do("HSET","student","name","luke")
fmt.Println(res,err)
res1,err := redis.String(conn.Do("HGET","student","name"))
fmt.Printf("res:%s,error:%v",res1,err)
}
//0 <nil>
//res:luke,error:<nil>
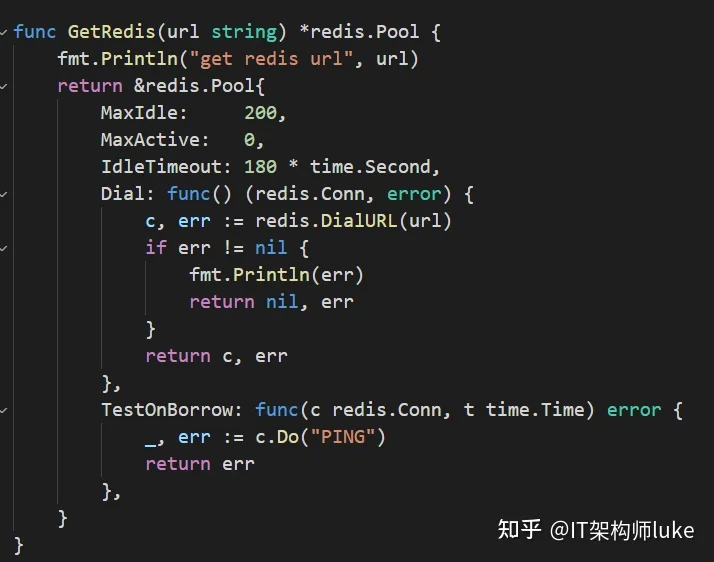
贴一份代码
如果你喜欢我写的技术文章以及面试总结,欢迎关注收看我的视频,并且点赞、收藏、关注我哦。
我是luke,感谢你的关注!
很多小伙伴在进阶的时候总会遇到一些问题和瓶颈,业务代码写多了没有方向感,不知道该从那里入手去提升,对此我整理了一些资料,希望能够去帮助到小伙伴们,可以关注我。并且加入到我的圈子一起学习成长哦【架构师之路】点击链接申请加入圈子
