1.OJ题的简述和其链接
1)括号匹配问题。OJ题链接
2)用队列实现栈。OJ题链接
3)用栈实现队列。OJ题链接
4)设计循环队列。OJ题链接
2.解题思路和代码
1)括号匹配问题

思路:
- 利用栈进行判断,首先我们创建一个新的栈
- 在遇到左括号的时候,放入栈里面
- 在遇到右括号的时候,出栈,并拿出栈的元素与其进行判断
- 如果有不相同的情况直接return false
- 注意特殊情况的处理:
1:如果,最后栈里面还剩左括号的元素,栈不为空,不符合要求,返回false
2:如果数组中只有右括号,在进行比较的时候,由于我们的栈里面没有元素,肯定会报错
所以需要在之前就进行一次判断,判断我们的栈是否为空,为空返回false就行
代码:
主要实现的函数:
bool isValid(char * s)
{//创建一个新的栈ST st;StackInit(&st);//如果*s为空退出循环while(*s){if(*s=='[' || *s=='(' || *s=='{'){StackPush(&st,*s);++s;}else{//如果数组中只有右括号,直接对栈进行判空操作if(StackEmpty(&st)){StackDestroy(&st);return false;}char top=StackTop(&st);StackPop(&st);//不匹配if( (*s == ']' && top != '[') || (*s == ')' && top != '(') || (*s == '}' && top != '{') ){StackDestroy(&st);return false;}else//继续{++s;}}}//如果,栈里面还剩左括号的元素,则说明不符合要求,所以要对栈进行判空操作bool ret =StackEmpty(&st);StackDestroy(&st);return ret;
}全部代码:
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>typedef char STDatatype;
typedef struct Stack
{STDatatype* a;int capacity;int top; // 初始为0,表示栈顶位置下一个位置下标
}ST;//初始化
void StackInit(ST* ps);//销毁
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);//入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDatatype x);//出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);//获取栈顶元素
STDatatype StackTop(ST* ps);//判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);void StackInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);ps->a = (STDatatype*)malloc(sizeof(STDatatype) * 4);if (ps->a == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 4;
}void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}void StackPush(ST* ps, STDatatype x)
{assert(ps);if (ps->top == ps->capacity){STDatatype* tmp = (STDatatype*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STDatatype));ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity *= 2;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}void StackPop(ST* ps)
{//判断栈是不是为NULLassert(ps);//判断栈里面还有没有元素assert(!StackEmpty(ps));ps->top--;
}STDatatype StackTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!StackEmpty(ps));//栈顶元素是top-1return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}bool isValid(char * s)
{//创建一个新的栈ST st;StackInit(&st);//如果*s为空退出循环while(*s){if(*s=='[' || *s=='(' || *s=='{'){StackPush(&st,*s);++s;}else{//如果数组中只有右括号,直接对栈进行判空操作if(StackEmpty(&st)){StackDestroy(&st);return false;}char top=StackTop(&st);StackPop(&st);//不匹配if( (*s == ']' && top != '[') || (*s == ')' && top != '(') || (*s == '}' && top != '{') ){StackDestroy(&st);return false;}else//继续{++s;}}}//如果,栈里面还剩左括号的元素,则说明不符合要求,所以要对栈进行判空操作bool ret =StackEmpty(&st);StackDestroy(&st);return ret;
}2)用队列实现栈

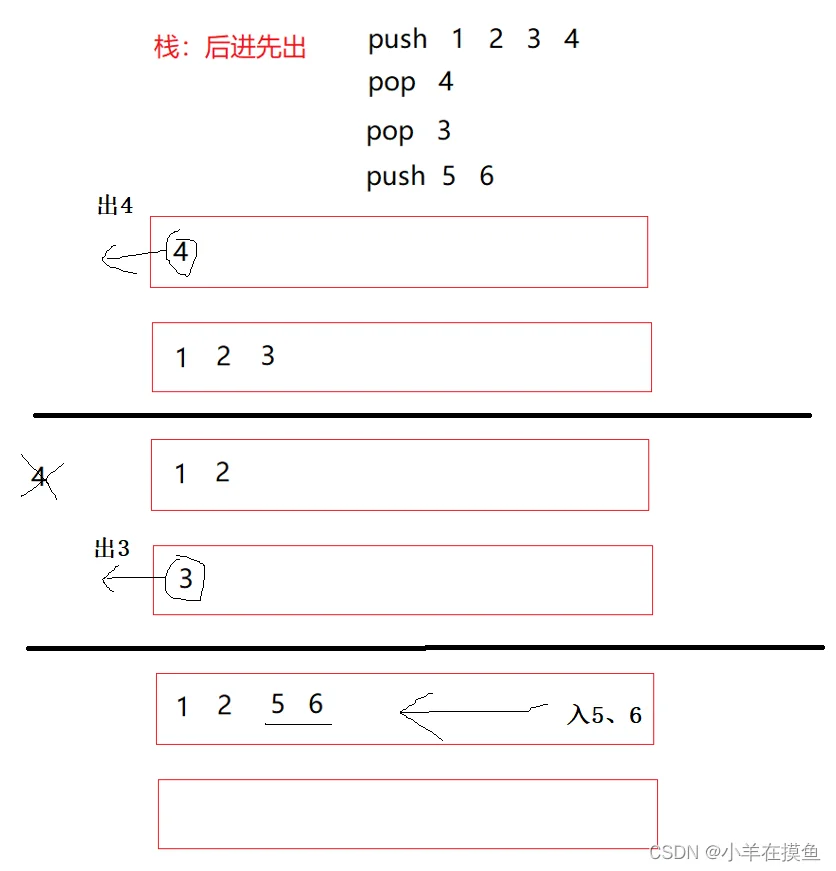
思路:
- 保持一个队列存数据,一个队列为空
- 入数据时,往不为空的队列里面加数据
- 出数据的时候,将有数据的队列导到空队列
- 画图说明如下:
主要代码的实现:
typedef struct
{Queue q1;Queue q2;
} MyStack;MyStack* myStackCreate()
{MyStack* obj=(MyStack *)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));QueueInit(&obj->q1);QueueInit(&obj->q2);return obj;
}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{//入数据,要往不为空的队列里面入if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);}else{QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);}
}int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
{//首先定义两个变量emptyQ(队列为空),nonemptyQ(队列不为空)Queue* emptyQ = &obj->q1;Queue* nonemptyQ = &obj->q2;//然后让emptyQ指向空队列,nonemptyQ指向不为空的队列if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){//如果q1队列不为空,则交换emptyQ = &obj->q2;nonemptyQ = &obj->q1;}//非空队列的前n-1个数据倒入空队列while(QueueSize(nonemptyQ) > 1){QueuePush(emptyQ,QueueFront(nonemptyQ));QueuePop(nonemptyQ);}//此时不为空队列剩,最后一个元素,用top接受并返回,实现栈的出数据int top = QueueFront(nonemptyQ);QueuePop(nonemptyQ);return top;
}int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{//栈顶元素,就数不为空队列的队尾元素if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){return QueueBack(&obj->q1);}else{return QueueBack(&obj->q2);}
}bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);free(obj);
}全部代码(多了队列的操作函数)
typedef int QDataType;typedef struct QueNode
{QDataType data;struct QueNode* next;
}QNode;typedef struct Queue
{QNode* head;QNode* tail;int size;
}Queue;// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);// 初始化队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);pq->head = NULL;pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}// 销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);QNode* cur = pq->head;while (cur){QNode* del = cur;cur = cur->next;free(del);}pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;pq->size = 0;
}// 队尾入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{assert(pq);QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;if (pq->tail == NULL){pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;}else{pq->tail->next = newnode;pq->tail = newnode;}pq->size++;
}// 队头出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));if (pq->head->next == NULL){free(pq->head);pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;}else{QNode* del = pq->head;pq->head = pq->head->next;free(del);}pq->size--;
}// 获取队列头部元素
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->head->data;
}// 获取队列队尾元素
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));return pq->tail->data;
}// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->head == NULL && pq->tail == NULL;
}// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{assert(pq);return pq->size;
}typedef struct
{Queue q1;Queue q2;
} MyStack;MyStack* myStackCreate()
{MyStack* obj=(MyStack *)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));QueueInit(&obj->q1);QueueInit(&obj->q2);return obj;
}void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{//入数据,要往不为空的队列里面入if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);}else{QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);}
}int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
{//首先定义两个变量emptyQ(队列为空),nonemptyQ(队列不为空)Queue* emptyQ = &obj->q1;Queue* nonemptyQ = &obj->q2;//然后让emptyQ指向空队列,nonemptyQ指向不为空的队列if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){//如果q1队列不为空,则交换emptyQ = &obj->q2;nonemptyQ = &obj->q1;}//非空队列的前n-1个数据倒入空队列while(QueueSize(nonemptyQ) > 1){QueuePush(emptyQ,QueueFront(nonemptyQ));QueuePop(nonemptyQ);}//此时不为空队列剩,最后一个元素,用top接受并返回,实现栈的出数据int top = QueueFront(nonemptyQ);QueuePop(nonemptyQ);return top;
}int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{//栈顶元素,就数不为空队列的队尾元素if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)){return QueueBack(&obj->q1);}else{return QueueBack(&obj->q2);}
}bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);free(obj);
}3)用栈实现队列

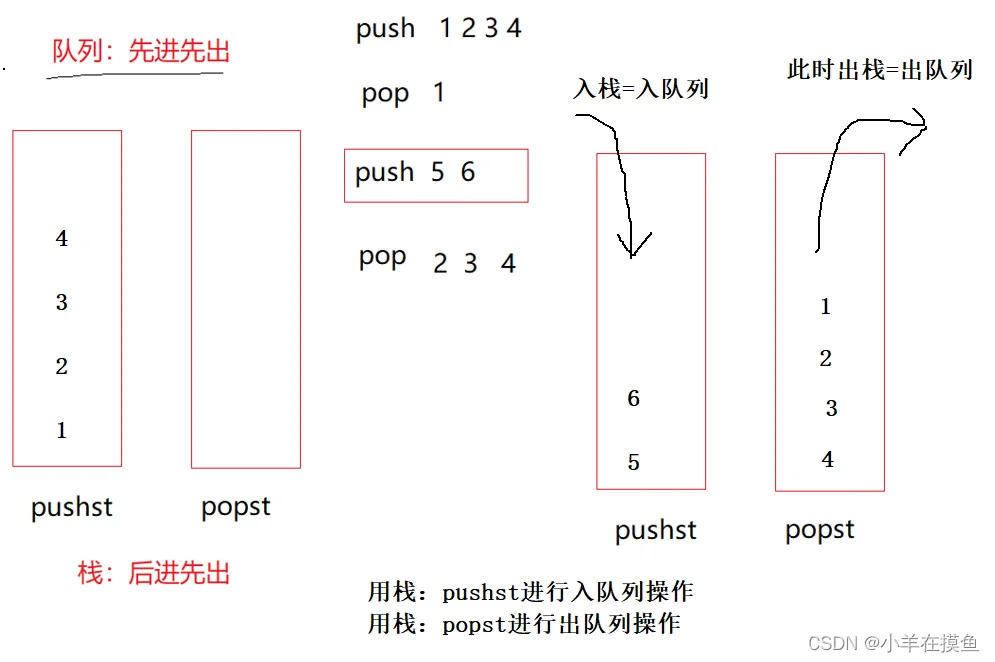
思路:
- 入队列,在pushST里面入,出队列,是把popST里面的直接出就行
主要实现代码:
typedef struct
{ST pushst;ST popst;
} MyQueue;bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj);
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj);MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{MyQueue* pq=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));StackInit(&pq->pushst);StackInit(&pq->popst);return pq;
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{assert(obj);//入队列,往pushst栈里面入StackPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));//用peek取栈popst的栈顶元素,并返回peek,栈popst的栈顶元素就是队列的队头元素int peek = myQueuePeek(obj);StackPop(&obj->popst);return peek;
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));//倒数据if(StackEmpty(&obj->popst)){while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushst)){StackPush(&obj->popst,StackTop(&obj->pushst));StackPop(&obj->pushst);}}return StackTop(&obj->popst);
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);return StackEmpty(&obj->pushst) && StackEmpty(&obj->popst);
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);StackDestroy(&obj->pushst);StackDestroy(&obj->popst);free(obj);
}全部代码(多了栈的操作函数)
typedef int STDatatype;
typedef struct Stack
{STDatatype* a;int capacity;int top; // 初始为0,表示栈顶位置下一个位置下标
}ST;//初始化
void StackInit(ST* ps);//销毁
void StackDestroy(ST* ps);//入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDatatype x);//出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);//获取栈顶元素
STDatatype StackTop(ST* ps);//栈中的有效个数
int StackSize(ST* ps);//判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);void StackInit(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);//也可以先给其开辟4个空间大小的地址ps->a = (STDatatype*)malloc(sizeof(STDatatype) * 4);if (ps->a == NULL){perror("malloc fail");exit(-1);}ps->top = 0;ps->capacity = 4;
}void StackDestroy(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);free(ps->a);ps->a = NULL;ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}void StackPush(ST* ps, STDatatype x)
{assert(ps);// 扩容//这里注意top是从0开始的,top指向的是顶的下一个,当存放了4个数据后,top=4(0,1,2,3)if (ps->top == ps->capacity){STDatatype* tmp = (STDatatype*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STDatatype));/*if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail");exit(-1);}*/ps->a = tmp;ps->capacity *= 2;}ps->a[ps->top] = x;ps->top++;
}void StackPop(ST* ps)
{//判断栈是不是为NULLassert(ps);//判断栈里面还有没有元素assert(!StackEmpty(ps));ps->top--;
}STDatatype StackTop(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);assert(!StackEmpty(ps));//栈顶元素是top-1return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}int StackSize(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top;
}bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{assert(ps);return ps->top == 0;
}typedef struct
{ST pushst;ST popst;
} MyQueue;bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj);
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj);MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{MyQueue* pq=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));StackInit(&pq->pushst);StackInit(&pq->popst);return pq;
}void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{assert(obj);//入队列,往pushst栈里面入StackPush(&obj->pushst,x);
}int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));//用peek取栈popst的栈顶元素,并返回peek,栈popst的栈顶元素就是队列的队头元素int peek = myQueuePeek(obj);StackPop(&obj->popst);return peek;
}int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);assert(!myQueueEmpty(obj));//倒数据if(StackEmpty(&obj->popst)){while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushst)){StackPush(&obj->popst,StackTop(&obj->pushst));StackPop(&obj->pushst);}}return StackTop(&obj->popst);
}bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);return StackEmpty(&obj->pushst) && StackEmpty(&obj->popst);
}void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);StackDestroy(&obj->pushst);StackDestroy(&obj->popst);free(obj);
}4)设计循环队列

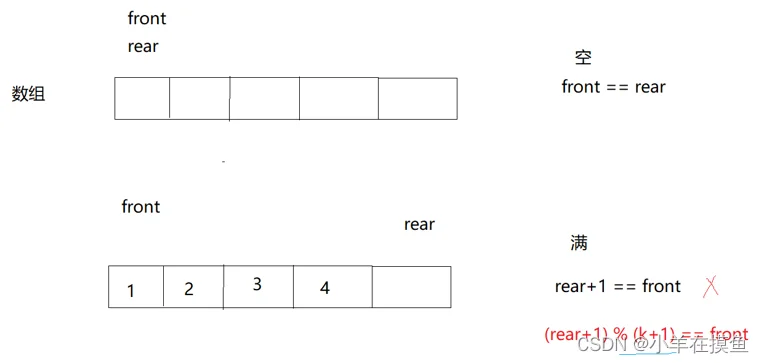
设计思路,循环队列一般用数组实现比较方便,
在判空的时候,如果 rear+1=front 为空,所以一般空间的大小都会比size大一个,用来判空。
在队头或队尾,走到数组最后面的时候,用%运算,来将其重新调回数组下标为0的位置
代码如下:
typedef struct
{int* data; //数组数据int front; //队头索引int rear; //对位索引int size; //队列大小
} MyCircularQueue;bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj);
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj);MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));//开辟数组空间的时候得多开一个obj->data = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (k + 1));obj->front = obj->rear = 0;//队列满的时候能存储数据k个数、其空间大小应该是k+1obj->size = k;return obj;
}bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{assert(obj);if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))return false;else{obj->data[obj->rear++] = value;//由于rear可能在数组的最后一个元素,//所以直接用%的方法来计算插入后的rear的位置obj->rear = obj->rear % (obj->size + 1);return true;}
}bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))return false;else{obj->front++;//假如此时front走到了最后位置,front++后就走到了数组外面,//此时front应该回到下标为0的位置,所以用一下的%运算来进行front的归位obj->front = obj->front % (obj->size + 1);return true;}
}int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}elsereturn obj->data[obj->front];
}int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);if (myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj)){return -1;}else//得到队尾的元素return obj->data[(obj->rear + obj->size) % (obj->size + 1)];
}bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);return obj->rear == obj->front;
}bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{assert(obj);//rear+1是rear的下一个位置,这里如果rear在数组最后的话,需要%5,//也就是size+1,让其返回到数组下标为0的位置return ((obj->rear + 1) % (obj->size + 1)) == obj->front;}void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{free(obj->data);free(obj);
}