func make(t Type, size ...IntegerType) Type
func new(Type) *Type
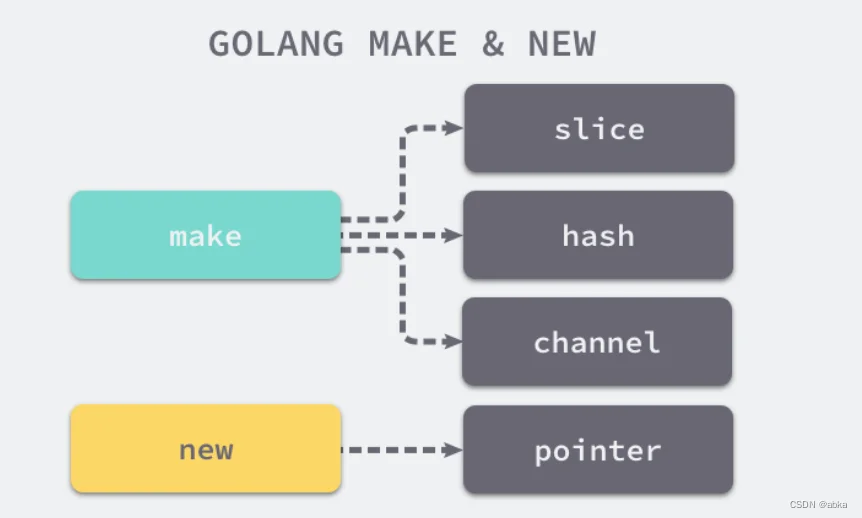
// The make built-in function allocates and initializes an object of type
// slice, map, or chan (only). Like new, the first argument is a type, not a
// value. Unlike new, make's return type is the same as the type of its
// argument, not a pointer to it. The specification of the result depends on
// the type:
// Slice: The size specifies the length. The capacity of the slice is
// equal to its length. A second integer argument may be provided to
// specify a different capacity; it must be no smaller than the
// length. For example, make([]int, 0, 10) allocates an underlying array
// of size 10 and returns a slice of length 0 and capacity 10 that is
// backed by this underlying array.
// Map: An empty map is allocated with enough space to hold the
// specified number of elements. The size may be omitted, in which case
// a small starting size is allocated.
// Channel: The channel's buffer is initialized with the specified
// buffer capacity. If zero, or the size is omitted, the channel is
// unbuffered.
func make(t Type, size ...IntegerType) Type
// The new built-in function allocates memory. The first argument is a type,
// not a value, and the value returned is a pointer to a newly
// allocated zero value of that type.
func new(Type) *Typemake 作用是初始化(非零值)内置的数据结构,被用来分配引用类型内存,也就是切片slice,哈希表map和channel
new的作用是根据传入类型分配一片内存空间并返回指向这片内存空间的指针,被用来分配除引用类型的所有其他类型的内存,内存置为0值(The new built-in function allocates memory. The first argument is a type, not a value, and the value returned is a pointer to a newly allocated zero value of that type.)
eg
slice := make([]int, 0, 100)
hash := make(map[int]bool, 10)
ch: = make(chan int, 5)
// 使用new
i := new(int)
// 这个等价于上面的
var v int
i := &v
new 通常不常用,可以使用短语句声明以及结构体的字面量达到目的
eg
i := 0
u: = user{}Make
make 初始化对象类别
go1.17.10.src/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/node.go
/*go1.17.10.src/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/node.go*/
OMAKE // make(Args) (before type checking converts to one of the following)
OMAKECHAN // make(Type[, Len]) (type is chan)
OMAKEMAP // make(Type[, Len]) (type is map)
OMAKESLICE // make(Type[, Len[, Cap]]) (type is slice)
OMAKESLICECOPY // makeslicecopy(Type, Len, Cap) (type is slice; Len is length and Cap is the copied from slice)
// OMAKESLICECOPY is created by the order pass and corresponds to:
// s = make(Type, Len); copy(s, Cap)
//
// Bounded can be set on the node when Len == len(Cap) is known at compile time.
//
// This node is created so the walk pass can optimize this pattern which would
// otherwise be hard to detect after the order pass.src/cmd/compile/internal/typecheck/typecheck.go:478
// typecheck1 should ONLY be called from typecheck.
func typecheck1(n ir.Node, top int) ir.Node 会进行替换
makeOMAKEOMAKESLICEOMAKEMAPOMAKECHAN// typecheck type checks node n.
// The result of typecheck MUST be assigned back to n, e.g.
// n.Left = typecheck(n.Left, top)
func typecheck(n ir.Node, top int) (res ir.Node) {
...
switch n.Op() {
...
case ir.OMAKE:
n := n.(*ir.CallExpr)
return tcMake(n)
case ir.ONEW:
n := n.(*ir.UnaryExpr)
return tcNew(n)
case ir.OMAKESLICECOPY:
n := n.(*ir.MakeExpr)
return tcMakeSliceCopy(n)
...
}
}go1.17.10.src/src/cmd/compile/internal/typecheck/func.go
// tcMake typechecks an OMAKE node.
func tcMake(n *ir.CallExpr) ir.Node {
args := n.Args
if len(args) == 0 {
base.Errorf("missing argument to make")
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
n.Args = nil
l := args[0]
l = typecheck(l, ctxType)
t := l.Type()
if t == nil {
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
i := 1
var nn ir.Node
switch t.Kind() {
default:
base.Errorf("cannot make type %v", t)
n.SetType(nil)
return n
case types.TSLICE:
if i >= len(args) {
base.Errorf("missing len argument to make(%v)", t)
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
l = args[i]
i++
l = Expr(l)
var r ir.Node
if i < len(args) {
r = args[i]
i++
r = Expr(r)
}
if l.Type() == nil || (r != nil && r.Type() == nil) {
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
if !checkmake(t, "len", &l) || r != nil && !checkmake(t, "cap", &r) {
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
if ir.IsConst(l, constant.Int) && r != nil && ir.IsConst(r, constant.Int) && constant.Compare(l.Val(), token.GTR, r.Val()) {
base.Errorf("len larger than cap in make(%v)", t)
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
nn = ir.NewMakeExpr(n.Pos(), ir.OMAKESLICE, l, r)
case types.TMAP:
if i < len(args) {
l = args[i]
i++
l = Expr(l)
l = DefaultLit(l, types.Types[types.TINT])
if l.Type() == nil {
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
if !checkmake(t, "size", &l) {
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
} else {
l = ir.NewInt(0)
}
nn = ir.NewMakeExpr(n.Pos(), ir.OMAKEMAP, l, nil)
nn.SetEsc(n.Esc())
case types.TCHAN:
l = nil
if i < len(args) {
l = args[i]
i++
l = Expr(l)
l = DefaultLit(l, types.Types[types.TINT])
if l.Type() == nil {
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
if !checkmake(t, "buffer", &l) {
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
} else {
l = ir.NewInt(0)
}
nn = ir.NewMakeExpr(n.Pos(), ir.OMAKECHAN, l, nil)
}
if i < len(args) {
base.Errorf("too many arguments to make(%v)", t)
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
nn.SetType(t)
return nn
}
// tcMakeSliceCopy typechecks an OMAKESLICECOPY node.
func tcMakeSliceCopy(n *ir.MakeExpr) ir.Node {
// Errors here are Fatalf instead of Errorf because only the compiler
// can construct an OMAKESLICECOPY node.
// Components used in OMAKESCLICECOPY that are supplied by parsed source code
// have already been typechecked in OMAKE and OCOPY earlier.
t := n.Type()
if t == nil {
base.Fatalf("no type specified for OMAKESLICECOPY")
}
if !t.IsSlice() {
base.Fatalf("invalid type %v for OMAKESLICECOPY", n.Type())
}
if n.Len == nil {
base.Fatalf("missing len argument for OMAKESLICECOPY")
}
if n.Cap == nil {
base.Fatalf("missing slice argument to copy for OMAKESLICECOPY")
}
n.Len = Expr(n.Len)
n.Cap = Expr(n.Cap)
n.Len = DefaultLit(n.Len, types.Types[types.TINT])
if !n.Len.Type().IsInteger() && n.Type().Kind() != types.TIDEAL {
base.Errorf("non-integer len argument in OMAKESLICECOPY")
}
if ir.IsConst(n.Len, constant.Int) {
if ir.ConstOverflow(n.Len.Val(), types.Types[types.TINT]) {
base.Fatalf("len for OMAKESLICECOPY too large")
}
if constant.Sign(n.Len.Val()) < 0 {
base.Fatalf("len for OMAKESLICECOPY must be non-negative")
}
}
return n
}
// tcNew typechecks an ONEW node.
func tcNew(n *ir.UnaryExpr) ir.Node {
if n.X == nil {
// Fatalf because the OCALL above checked for us,
// so this must be an internally-generated mistake.
base.Fatalf("missing argument to new")
}
l := n.X
l = typecheck(l, ctxType)
t := l.Type()
if t == nil {
n.SetType(nil)
return n
}
n.X = l
n.SetType(types.NewPtr(t))
return n
}go1.17.10.src/src/cmd/compile/internal/typecheck/typecheck.go
// typecheck type checks node n.
// The result of typecheck MUST be assigned back to n, e.g.
// n.Left = typecheck(n.Left, top)
func typecheck(n ir.Node, top int) (res ir.Node) {
// cannot type check until all the source has been parsed
if !TypecheckAllowed {
base.Fatalf("early typecheck")
}
if n == nil {
return nil
}
// only trace if there's work to do
if base.EnableTrace && base.Flag.LowerT {
defer tracePrint("typecheck", n)(&res)
}
lno := ir.SetPos(n)
// Skip over parens.
for n.Op() == ir.OPAREN {
n = n.(*ir.ParenExpr).X
}
// Resolve definition of name and value of iota lazily.
n = Resolve(n)
// Skip typecheck if already done.
// But re-typecheck ONAME/OTYPE/OLITERAL/OPACK node in case context has changed.
if n.Typecheck() == 1 || n.Typecheck() == 3 {
switch n.Op() {
case ir.ONAME, ir.OTYPE, ir.OLITERAL, ir.OPACK:
break
default:
base.Pos = lno
return n
}
}
if n.Typecheck() == 2 {
// Typechecking loop. Trying printing a meaningful message,
// otherwise a stack trace of typechecking.
switch n.Op() {
// We can already diagnose variables used as types.
case ir.ONAME:
n := n.(*ir.Name)
if top&(ctxExpr|ctxType) == ctxType {
base.Errorf("%v is not a type", n)
}
case ir.OTYPE:
// Only report a type cycle if we are expecting a type.
// Otherwise let other code report an error.
if top&ctxType == ctxType {
// A cycle containing only alias types is an error
// since it would expand indefinitely when aliases
// are substituted.
cycle := cycleFor(n)
for _, n1 := range cycle {
if n1.Name() != nil && !n1.Name().Alias() {
// Cycle is ok. But if n is an alias type and doesn't
// have a type yet, we have a recursive type declaration
// with aliases that we can't handle properly yet.
// Report an error rather than crashing later.
if n.Name() != nil && n.Name().Alias() && n.Type() == nil {
base.Pos = n.Pos()
base.Fatalf("cannot handle alias type declaration (issue #25838): %v", n)
}
base.Pos = lno
return n
}
}
base.ErrorfAt(n.Pos(), "invalid recursive type alias %v%s", n, cycleTrace(cycle))
}
case ir.OLITERAL:
if top&(ctxExpr|ctxType) == ctxType {
base.Errorf("%v is not a type", n)
break
}
base.ErrorfAt(n.Pos(), "constant definition loop%s", cycleTrace(cycleFor(n)))
}
if base.Errors() == 0 {
var trace string
for i := len(typecheck_tcstack) - 1; i >= 0; i-- {
x := typecheck_tcstack[i]
trace += fmt.Sprintf("\n\t%v %v", ir.Line(x), x)
}
base.Errorf("typechecking loop involving %v%s", n, trace)
}
base.Pos = lno
return n
}
typecheck_tcstack = append(typecheck_tcstack, n)
n.SetTypecheck(2)
n = typecheck1(n, top)
n.SetTypecheck(1)
last := len(typecheck_tcstack) - 1
typecheck_tcstack[last] = nil
typecheck_tcstack = typecheck_tcstack[:last]
_, isExpr := n.(ir.Expr)
_, isStmt := n.(ir.Stmt)
isMulti := false
switch n.Op() {
case ir.OCALLFUNC, ir.OCALLINTER, ir.OCALLMETH:
n := n.(*ir.CallExpr)
if t := n.X.Type(); t != nil && t.Kind() == types.TFUNC {
nr := t.NumResults()
isMulti = nr > 1
if nr == 0 {
isExpr = false
}
}
case ir.OAPPEND:
// Must be used (and not BinaryExpr/UnaryExpr).
isStmt = false
case ir.OCLOSE, ir.ODELETE, ir.OPANIC, ir.OPRINT, ir.OPRINTN, ir.OVARKILL, ir.OVARLIVE:
// Must not be used.
isExpr = false
isStmt = true
case ir.OCOPY, ir.ORECOVER, ir.ORECV:
// Can be used or not.
isStmt = true
}
t := n.Type()
if t != nil && !t.IsFuncArgStruct() && n.Op() != ir.OTYPE {
switch t.Kind() {
case types.TFUNC, // might have TANY; wait until it's called
types.TANY, types.TFORW, types.TIDEAL, types.TNIL, types.TBLANK:
break
default:
types.CheckSize(t)
}
}
if t != nil {
n = EvalConst(n)
t = n.Type()
}
// TODO(rsc): Lots of the complexity here is because typecheck can
// see OTYPE, ONAME, and OLITERAL nodes multiple times.
// Once we make the IR a proper tree, we should be able to simplify
// this code a bit, especially the final case.
switch {
case top&(ctxStmt|ctxExpr) == ctxExpr && !isExpr && n.Op() != ir.OTYPE && !isMulti:
if !n.Diag() {
base.Errorf("%v used as value", n)
n.SetDiag(true)
}
if t != nil {
n.SetType(nil)
}
case top&ctxType == 0 && n.Op() == ir.OTYPE && t != nil:
if !n.Type().Broke() {
base.Errorf("type %v is not an expression", n.Type())
n.SetDiag(true)
}
case top&(ctxStmt|ctxExpr) == ctxStmt && !isStmt && t != nil:
if !n.Diag() {
base.Errorf("%v evaluated but not used", n)
n.SetDiag(true)
}
n.SetType(nil)
case top&(ctxType|ctxExpr) == ctxType && n.Op() != ir.OTYPE && n.Op() != ir.ONONAME && (t != nil || n.Op() == ir.ONAME):
base.Errorf("%v is not a type", n)
if t != nil {
if n.Op() == ir.ONAME {
t.SetBroke(true)
} else {
n.SetType(nil)
}
}
}
base.Pos = lno
return n
}go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/expr.go
// go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/mini.go
// A miniNode is a minimal node implementation,
// meant to be embedded as the first field in a larger node implementation,
// at a cost of 8 bytes.
//
// A miniNode is NOT a valid Node by itself: the embedding struct
// must at the least provide:
//
// func (n *MyNode) String() string { return fmt.Sprint(n) }
// func (n *MyNode) rawCopy() Node { c := *n; return &c }
// func (n *MyNode) Format(s fmt.State, verb rune) { FmtNode(n, s, verb) }
//
// The embedding struct should also fill in n.op in its constructor,
// for more useful panic messages when invalid methods are called,
// instead of implementing Op itself.
//
type miniNode struct {
pos src.XPos // uint32
op Op // uint8
bits bitset8
esc uint16
}
go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/expr.go
---------
// go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/expr.go
// A miniExpr is a miniNode with extra fields common to expressions.
// TODO(rsc): Once we are sure about the contents, compact the bools
// into a bit field and leave extra bits available for implementations
// embedding miniExpr. Right now there are ~60 unused bits sitting here.
type miniExpr struct {
miniNode
typ *types.Type
init Nodes // TODO(rsc): Don't require every Node to have an init
flags bitset8
}
// A MakeExpr is a make expression: make(Type[, Len[, Cap]]).
// Op is OMAKECHAN, OMAKEMAP, OMAKESLICE, or OMAKESLICECOPY,
// but *not* OMAKE (that's a pre-typechecking CallExpr).
type MakeExpr struct {
miniExpr
Len Node
Cap Node
}
func NewMakeExpr(pos src.XPos, op Op, len, cap Node) *MakeExpr {
n := &MakeExpr{Len: len, Cap: cap}
n.pos = pos
n.SetOp(op)
return n
}go1.18.1/go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/node.go
//go:generate stringer -type=Op -trimprefix=O node.go
type Op uint8
// Node ops.
const (
OXXX Op = iota
// names
ONAME // var or func name
// Unnamed arg or return value: f(int, string) (int, error) { etc }
// Also used for a qualified package identifier that hasn't been resolved yet.
ONONAME
OTYPE // type name
OPACK // import
OLITERAL // literal
ONIL // nil
// expressions
OADD // X + Y
OSUB // X - Y
OOR // X | Y
OXOR // X ^ Y
OADDSTR // +{List} (string addition, list elements are strings)
OADDR // &X
OANDAND // X && Y
OAPPEND // append(Args); after walk, X may contain elem type descriptor
OBYTES2STR // Type(X) (Type is string, X is a []byte)
OBYTES2STRTMP // Type(X) (Type is string, X is a []byte, ephemeral)
ORUNES2STR // Type(X) (Type is string, X is a []rune)
OSTR2BYTES // Type(X) (Type is []byte, X is a string)
OSTR2BYTESTMP // Type(X) (Type is []byte, X is a string, ephemeral)
OSTR2RUNES // Type(X) (Type is []rune, X is a string)
OSLICE2ARRPTR // Type(X) (Type is *[N]T, X is a []T)
// X = Y or (if Def=true) X := Y
// If Def, then Init includes a DCL node for X.
OAS
// Lhs = Rhs (x, y, z = a, b, c) or (if Def=true) Lhs := Rhs
// If Def, then Init includes DCL nodes for Lhs
OAS2
OAS2DOTTYPE // Lhs = Rhs (x, ok = I.(int))
OAS2FUNC // Lhs = Rhs (x, y = f())
OAS2MAPR // Lhs = Rhs (x, ok = m["foo"])
OAS2RECV // Lhs = Rhs (x, ok = <-c)
OASOP // X AsOp= Y (x += y)
OCALL // X(Args) (function call, method call or type conversion)
// OCALLFUNC, OCALLMETH, and OCALLINTER have the same structure.
// Prior to walk, they are: X(Args), where Args is all regular arguments.
// After walk, if any argument whose evaluation might requires temporary variable,
// that temporary variable will be pushed to Init, Args will contains an updated
// set of arguments. KeepAlive is all OVARLIVE nodes that are attached to OCALLxxx.
OCALLFUNC // X(Args) (function call f(args))
OCALLMETH // X(Args) (direct method call x.Method(args))
OCALLINTER // X(Args) (interface method call x.Method(args))
OCAP // cap(X)
OCLOSE // close(X)
OCLOSURE // func Type { Func.Closure.Body } (func literal)
OCOMPLIT // Type{List} (composite literal, not yet lowered to specific form)
OMAPLIT // Type{List} (composite literal, Type is map)
OSTRUCTLIT // Type{List} (composite literal, Type is struct)
OARRAYLIT // Type{List} (composite literal, Type is array)
OSLICELIT // Type{List} (composite literal, Type is slice), Len is slice length.
OPTRLIT // &X (X is composite literal)
OCONV // Type(X) (type conversion)
OCONVIFACE // Type(X) (type conversion, to interface)
OCONVIDATA // Builds a data word to store X in an interface. Equivalent to IDATA(CONVIFACE(X)). Is an ir.ConvExpr.
OCONVNOP // Type(X) (type conversion, no effect)
OCOPY // copy(X, Y)
ODCL // var X (declares X of type X.Type)
// Used during parsing but don't last.
ODCLFUNC // func f() or func (r) f()
ODCLCONST // const pi = 3.14
ODCLTYPE // type Int int or type Int = int
ODELETE // delete(Args)
ODOT // X.Sel (X is of struct type)
ODOTPTR // X.Sel (X is of pointer to struct type)
ODOTMETH // X.Sel (X is non-interface, Sel is method name)
ODOTINTER // X.Sel (X is interface, Sel is method name)
OXDOT // X.Sel (before rewrite to one of the preceding)
ODOTTYPE // X.Ntype or X.Type (.Ntype during parsing, .Type once resolved); after walk, Itab contains address of interface type descriptor and Itab.X contains address of concrete type descriptor
ODOTTYPE2 // X.Ntype or X.Type (.Ntype during parsing, .Type once resolved; on rhs of OAS2DOTTYPE); after walk, Itab contains address of interface type descriptor
OEQ // X == Y
ONE // X != Y
OLT // X < Y
OLE // X <= Y
OGE // X >= Y
OGT // X > Y
ODEREF // *X
OINDEX // X[Index] (index of array or slice)
OINDEXMAP // X[Index] (index of map)
OKEY // Key:Value (key:value in struct/array/map literal)
OSTRUCTKEY // Field:Value (key:value in struct literal, after type checking)
OLEN // len(X)
OMAKE // make(Args) (before type checking converts to one of the following)
OMAKECHAN // make(Type[, Len]) (type is chan)
OMAKEMAP // make(Type[, Len]) (type is map)
OMAKESLICE // make(Type[, Len[, Cap]]) (type is slice)
OMAKESLICECOPY // makeslicecopy(Type, Len, Cap) (type is slice; Len is length and Cap is the copied from slice)
// OMAKESLICECOPY is created by the order pass and corresponds to:
// s = make(Type, Len); copy(s, Cap)
//
// Bounded can be set on the node when Len == len(Cap) is known at compile time.
//
// This node is created so the walk pass can optimize this pattern which would
// otherwise be hard to detect after the order pass.
OMUL // X * Y
ODIV // X / Y
OMOD // X % Y
OLSH // X << Y
ORSH // X >> Y
OAND // X & Y
OANDNOT // X &^ Y
ONEW // new(X); corresponds to calls to new in source code
ONOT // !X
OBITNOT // ^X
OPLUS // +X
ONEG // -X
OOROR // X || Y
OPANIC // panic(X)
OPRINT // print(List)
OPRINTN // println(List)
OPAREN // (X)
OSEND // Chan <- Value
OSLICE // X[Low : High] (X is untypechecked or slice)
OSLICEARR // X[Low : High] (X is pointer to array)
OSLICESTR // X[Low : High] (X is string)
OSLICE3 // X[Low : High : Max] (X is untypedchecked or slice)
OSLICE3ARR // X[Low : High : Max] (X is pointer to array)
OSLICEHEADER // sliceheader{Ptr, Len, Cap} (Ptr is unsafe.Pointer, Len is length, Cap is capacity)
ORECOVER // recover()
ORECOVERFP // recover(Args) w/ explicit FP argument
ORECV // <-X
ORUNESTR // Type(X) (Type is string, X is rune)
OSELRECV2 // like OAS2: Lhs = Rhs where len(Lhs)=2, len(Rhs)=1, Rhs[0].Op = ORECV (appears as .Var of OCASE)
OIOTA // iota
OREAL // real(X)
OIMAG // imag(X)
OCOMPLEX // complex(X, Y)
OALIGNOF // unsafe.Alignof(X)
OOFFSETOF // unsafe.Offsetof(X)
OSIZEOF // unsafe.Sizeof(X)
OUNSAFEADD // unsafe.Add(X, Y)
OUNSAFESLICE // unsafe.Slice(X, Y)
OMETHEXPR // X(Args) (method expression T.Method(args), first argument is the method receiver)
OMETHVALUE // X.Sel (method expression t.Method, not called)
// statements
OBLOCK // { List } (block of code)
OBREAK // break [Label]
// OCASE: case List: Body (List==nil means default)
// For OTYPESW, List is a OTYPE node for the specified type (or OLITERAL
// for nil) or an ODYNAMICTYPE indicating a runtime type for generics.
// If a type-switch variable is specified, Var is an
// ONAME for the version of the type-switch variable with the specified
// type.
OCASE
OCONTINUE // continue [Label]
ODEFER // defer Call
OFALL // fallthrough
OFOR // for Init; Cond; Post { Body }
// OFORUNTIL is like OFOR, but the test (Cond) is applied after the body:
// Init
// top: { Body } // Execute the body at least once
// cont: Post
// if Cond { // And then test the loop condition
// List // Before looping to top, execute List
// goto top
// }
// OFORUNTIL is created by walk. There's no way to write this in Go code.
OFORUNTIL
OGOTO // goto Label
OIF // if Init; Cond { Then } else { Else }
OLABEL // Label:
OGO // go Call
ORANGE // for Key, Value = range X { Body }
ORETURN // return Results
OSELECT // select { Cases }
OSWITCH // switch Init; Expr { Cases }
// OTYPESW: X := Y.(type) (appears as .Tag of OSWITCH)
// X is nil if there is no type-switch variable
OTYPESW
OFUNCINST // instantiation of a generic function
// types
OTCHAN // chan int
OTMAP // map[string]int
OTSTRUCT // struct{}
OTINTER // interface{}
// OTFUNC: func() - Recv is receiver field, Params is list of param fields, Results is
// list of result fields.
OTFUNC
OTARRAY // [8]int or [...]int
OTSLICE // []int
// misc
// intermediate representation of an inlined call. Uses Init (assignments
// for the captured variables, parameters, retvars, & INLMARK op),
// Body (body of the inlined function), and ReturnVars (list of
// return values)
OINLCALL // intermediary representation of an inlined call.
OEFACE // itable and data words of an empty-interface value.
OITAB // itable word of an interface value.
OIDATA // data word of an interface value in X
OSPTR // base pointer of a slice or string.
OCFUNC // reference to c function pointer (not go func value)
OCHECKNIL // emit code to ensure pointer/interface not nil
OVARDEF // variable is about to be fully initialized
OVARKILL // variable is dead
OVARLIVE // variable is alive
ORESULT // result of a function call; Xoffset is stack offset
OINLMARK // start of an inlined body, with file/line of caller. Xoffset is an index into the inline tree.
OLINKSYMOFFSET // offset within a name
// opcodes for generics
ODYNAMICDOTTYPE // x = i.(T) where T is a type parameter (or derived from a type parameter)
ODYNAMICDOTTYPE2 // x, ok = i.(T) where T is a type parameter (or derived from a type parameter)
ODYNAMICTYPE // a type node for type switches (represents a dynamic target type for a type switch)
// arch-specific opcodes
OTAILCALL // tail call to another function
OGETG // runtime.getg() (read g pointer)
OGETCALLERPC // runtime.getcallerpc() (continuation PC in caller frame)
OGETCALLERSP // runtime.getcallersp() (stack pointer in caller frame)
OEND
)New
new 对应的 OP type 是 ONEW,walkexpr()会根据是否需要逃逸到堆上来分别处理,需要逃逸到堆上的话调用 callnew(),不需要的话直接在栈上分配
go1.17.10.src/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/node.go
ONEW // new(X); corresponds to calls to new in source code
go1.18.1/go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/walk/expr.go
func walkExpr1(n ir.Node, init *ir.Nodes) ir.Node {
switch n.Op() {
...
case ir.ONEW:
n := n.(*ir.UnaryExpr)
return walkNew(n, init)
...
}
}go1.18.1/go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/walk/builtin.go
// walkNew walks an ONEW node.
func walkNew(n *ir.UnaryExpr, init *ir.Nodes) ir.Node {
t := n.Type().Elem()
if t.NotInHeap() {
base.Errorf("%v can't be allocated in Go; it is incomplete (or unallocatable)", n.Type().Elem())
}
if n.Esc() == ir.EscNone {
if t.Size() > ir.MaxImplicitStackVarSize {
base.Fatalf("large ONEW with EscNone: %v", n)
}
return stackTempAddr(init, t)
}
types.CalcSize(t)
n.MarkNonNil()
return n
}
go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/walk/temp.go
// stackTempAddr returns the expression &tmp, where tmp is a newly
// allocated temporary variable of the given type. Statements to
// zero-initialize tmp are appended to init.
func stackTempAddr(init *ir.Nodes, typ *types.Type) *ir.AddrExpr {
return initStackTemp(init, typecheck.Temp(typ), nil)
}
// initStackTemp appends statements to init to initialize the given
// temporary variable to val, and then returns the expression &tmp.
func initStackTemp(init *ir.Nodes, tmp *ir.Name, val ir.Node) *ir.AddrExpr {
if val != nil && !types.Identical(tmp.Type(), val.Type()) {
base.Fatalf("bad initial value for %L: %L", tmp, val)
}
appendWalkStmt(init, ir.NewAssignStmt(base.Pos, tmp, val))
return typecheck.Expr(typecheck.NodAddr(tmp)).(*ir.AddrExpr)
}
go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/walk/walk.go
// appendWalkStmt typechecks and walks stmt and then appends it to init.
func appendWalkStmt(init *ir.Nodes, stmt ir.Node) {
op := stmt.Op()
n := typecheck.Stmt(stmt)
if op == ir.OAS || op == ir.OAS2 {
// If the assignment has side effects, walkExpr will append them
// directly to init for us, while walkStmt will wrap it in an OBLOCK.
// We need to append them directly.
// TODO(rsc): Clean this up.
n = walkExpr(n, init)
} else {
n = walkStmt(n)
}
init.Append(n)
}go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/walk/expr.go
// The result of walkExpr MUST be assigned back to n, e.g.
// n.Left = walkExpr(n.Left, init)
func walkExpr(n ir.Node, init *ir.Nodes) ir.Node {
if n == nil {
return n
}
if n, ok := n.(ir.InitNode); ok && init == n.PtrInit() {
// not okay to use n->ninit when walking n,
// because we might replace n with some other node
// and would lose the init list.
base.Fatalf("walkExpr init == &n->ninit")
}
if len(n.Init()) != 0 {
walkStmtList(n.Init())
init.Append(ir.TakeInit(n)...)
}
lno := ir.SetPos(n)
if base.Flag.LowerW > 1 {
ir.Dump("before walk expr", n)
}
if n.Typecheck() != 1 {
base.Fatalf("missed typecheck: %+v", n)
}
if n.Type().IsUntyped() {
base.Fatalf("expression has untyped type: %+v", n)
}
n = walkExpr1(n, init)
// Eagerly compute sizes of all expressions for the back end.
if typ := n.Type(); typ != nil && typ.Kind() != types.TBLANK && !typ.IsFuncArgStruct() {
types.CheckSize(typ)
}
if n, ok := n.(*ir.Name); ok && n.Heapaddr != nil {
types.CheckSize(n.Heapaddr.Type())
}
if ir.IsConst(n, constant.String) {
// Emit string symbol now to avoid emitting
// any concurrently during the backend.
_ = staticdata.StringSym(n.Pos(), constant.StringVal(n.Val()))
}
if base.Flag.LowerW != 0 && n != nil {
ir.Dump("after walk expr", n)
}
base.Pos = lno
return n
}go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/walk/stmt.go
// The result of walkStmt MUST be assigned back to n, e.g.
// n.Left = walkStmt(n.Left)
func walkStmt(n ir.Node) ir.Node {
if n == nil {
return n
}
ir.SetPos(n)
walkStmtList(n.Init())
switch n.Op() {
default:
if n.Op() == ir.ONAME {
n := n.(*ir.Name)
base.Errorf("%v is not a top level statement", n.Sym())
} else {
base.Errorf("%v is not a top level statement", n.Op())
}
ir.Dump("nottop", n)
return n
case ir.OAS,
ir.OASOP,
ir.OAS2,
ir.OAS2DOTTYPE,
ir.OAS2RECV,
ir.OAS2FUNC,
ir.OAS2MAPR,
ir.OCLOSE,
ir.OCOPY,
ir.OCALLINTER,
ir.OCALL,
ir.OCALLFUNC,
ir.ODELETE,
ir.OSEND,
ir.OPRINT,
ir.OPRINTN,
ir.OPANIC,
ir.ORECOVERFP,
ir.OGETG:
if n.Typecheck() == 0 {
base.Fatalf("missing typecheck: %+v", n)
}
init := ir.TakeInit(n)
n = walkExpr(n, &init)
if n.Op() == ir.ONAME {
// copy rewrote to a statement list and a temp for the length.
// Throw away the temp to avoid plain values as statements.
n = ir.NewBlockStmt(n.Pos(), init)
init = nil
}
if len(init) > 0 {
switch n.Op() {
case ir.OAS, ir.OAS2, ir.OBLOCK:
n.(ir.InitNode).PtrInit().Prepend(init...)
default:
init.Append(n)
n = ir.NewBlockStmt(n.Pos(), init)
}
}
return n
// special case for a receive where we throw away
// the value received.
case ir.ORECV:
n := n.(*ir.UnaryExpr)
return walkRecv(n)
case ir.OBREAK,
ir.OCONTINUE,
ir.OFALL,
ir.OGOTO,
ir.OLABEL,
ir.ODCL,
ir.ODCLCONST,
ir.ODCLTYPE,
ir.OCHECKNIL,
ir.OVARDEF,
ir.OVARKILL,
ir.OVARLIVE:
return n
case ir.OBLOCK:
n := n.(*ir.BlockStmt)
walkStmtList(n.List)
return n
case ir.OCASE:
base.Errorf("case statement out of place")
panic("unreachable")
case ir.ODEFER:
n := n.(*ir.GoDeferStmt)
ir.CurFunc.SetHasDefer(true)
ir.CurFunc.NumDefers++
if ir.CurFunc.NumDefers > maxOpenDefers {
// Don't allow open-coded defers if there are more than
// 8 defers in the function, since we use a single
// byte to record active defers.
ir.CurFunc.SetOpenCodedDeferDisallowed(true)
}
if n.Esc() != ir.EscNever {
// If n.Esc is not EscNever, then this defer occurs in a loop,
// so open-coded defers cannot be used in this function.
ir.CurFunc.SetOpenCodedDeferDisallowed(true)
}
fallthrough
case ir.OGO:
n := n.(*ir.GoDeferStmt)
return walkGoDefer(n)
case ir.OFOR, ir.OFORUNTIL:
n := n.(*ir.ForStmt)
return walkFor(n)
case ir.OIF:
n := n.(*ir.IfStmt)
return walkIf(n)
case ir.ORETURN:
n := n.(*ir.ReturnStmt)
return walkReturn(n)
case ir.OTAILCALL:
n := n.(*ir.TailCallStmt)
var init ir.Nodes
n.Call.X = walkExpr(n.Call.X, &init)
if len(init) > 0 {
init.Append(n)
return ir.NewBlockStmt(n.Pos(), init)
}
return n
case ir.OINLMARK:
n := n.(*ir.InlineMarkStmt)
return n
case ir.OSELECT:
n := n.(*ir.SelectStmt)
walkSelect(n)
return n
case ir.OSWITCH:
n := n.(*ir.SwitchStmt)
walkSwitch(n)
return n
case ir.ORANGE:
n := n.(*ir.RangeStmt)
return walkRange(n)
}
// No return! Each case must return (or panic),
// to avoid confusion about what gets returned
// in the presence of type assertions.
go1.18.1/go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/types/type.go
// A Type represents a Go type.
//
// There may be multiple unnamed types with identical structure. However, there must
// be a unique Type object for each unique named (defined) type. After noding, a
// package-level type can be looked up by building its unique symbol sym (sym =
// package.Lookup(name)) and checking sym.Def. If sym.Def is non-nil, the type
// already exists at package scope and is available at sym.Def.(*ir.Name).Type().
// Local types (which may have the same name as a package-level type) are
// distinguished by the value of vargen.
type Type struct {
// extra contains extra etype-specific fields.
// As an optimization, those etype-specific structs which contain exactly
// one pointer-shaped field are stored as values rather than pointers when possible.
//
// TMAP: *Map
// TFORW: *Forward
// TFUNC: *Func
// TSTRUCT: *Struct
// TINTER: *Interface
// TFUNCARGS: FuncArgs
// TCHANARGS: ChanArgs
// TCHAN: *Chan
// TPTR: Ptr
// TARRAY: *Array
// TSLICE: Slice
// TSSA: string
// TTYPEPARAM: *Typeparam
// TUNION: *Union
extra interface{}
// width is the width of this Type in bytes.
width int64 // valid if Align > 0
// list of base methods (excluding embedding)
methods Fields
// list of all methods (including embedding)
allMethods Fields
// canonical OTYPE node for a named type (should be an ir.Name node with same sym)
nod Object
// the underlying type (type literal or predeclared type) for a defined type
underlying *Type
// Cache of composite types, with this type being the element type.
cache struct {
ptr *Type // *T, or nil
slice *Type // []T, or nil
}
sym *Sym // symbol containing name, for named types
vargen int32 // unique name for OTYPE/ONAME
kind Kind // kind of type
align uint8 // the required alignment of this type, in bytes (0 means Width and Align have not yet been computed)
flags bitset8
// For defined (named) generic types, a pointer to the list of type params
// (in order) of this type that need to be instantiated. For instantiated
// generic types, this is the targs used to instantiate them. These targs
// may be typeparams (for re-instantiated types such as Value[T2]) or
// concrete types (for fully instantiated types such as Value[int]).
// rparams is only set for named types that are generic or are fully
// instantiated from a generic type, and is otherwise set to nil.
// TODO(danscales): choose a better name.
rparams *[]*Type
// For an instantiated generic type, the base generic type.
// This backpointer is useful, because the base type is the type that has
// the method bodies.
origType *Type
}
const (
typeNotInHeap = 1 << iota // type cannot be heap allocated
typeBroke // broken type definition
typeNoalg // suppress hash and eq algorithm generation
typeDeferwidth // width computation has been deferred and type is on deferredTypeStack
typeRecur
typeHasTParam // there is a typeparam somewhere in the type (generic function or type)
typeIsShape // represents a set of closely related types, for generics
typeHasShape // there is a shape somewhere in the type
)
func (t *Type) NotInHeap() bool { return t.flags&typeNotInHeap != 0 }
go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/types/utils.go
type bitset8 uint8
func (f *bitset8) set(mask uint8, b bool) {
if b {
*(*uint8)(f) |= mask
} else {
*(*uint8)(f) &^= mask
}
}go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/expr.go
// A UnaryExpr is a unary expression Op X,
// or Op(X) for a builtin function that does not end up being a call.
type UnaryExpr struct {
miniExpr
X Node
}go1.18.1/src/cmd/compile/internal/ir/node.go
// A Node is the abstract interface to an IR node.
type Node interface {
// Formatting
Format(s fmt.State, verb rune)
// Source position.
Pos() src.XPos
SetPos(x src.XPos)
// For making copies. For Copy and SepCopy.
copy() Node
doChildren(func(Node) bool) bool
editChildren(func(Node) Node)
// Abstract graph structure, for generic traversals.
Op() Op
Init() Nodes
// Fields specific to certain Ops only.
Type() *types.Type
SetType(t *types.Type)
Name() *Name
Sym() *types.Sym
Val() constant.Value
SetVal(v constant.Value)
// Storage for analysis passes.
Esc() uint16
SetEsc(x uint16)
Diag() bool
SetDiag(x bool)
// Typecheck values:
// 0 means the node is not typechecked
// 1 means the node is completely typechecked
// 2 means typechecking of the node is in progress
// 3 means the node has its type from types2, but may need transformation
Typecheck() uint8
SetTypecheck(x uint8)
NonNil() bool
MarkNonNil()
}