01 Hello World
gogorun.gobuildgo buildpackage main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello World!")
}
go get golang.org/x/tools/cmd/goimports
02 命令行参数
for initialization; condition; post{
// zero or more statements
}
// a traditional "while" loop
for condition {
// ...
}
// a traditional infinite loop
for {
// ...
}
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
s, sep := "", ""
for _, arg := range os.Args[1:] {
s += sep + arg
sep = " "
}
fmt.Println(s)
}
func main() {
fmt.Println(strings.Join(os.Args[1:], " "))
}
练习
echo 程序
// Echo1 prints its command-line arguments.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
var s, sep string
for i := 1; i < len(os.Args); i++ {
s += sep + os.Args[i]
sep = " "
}
fmt.Println(s)
}
练习1.1
echoos.Args[0]func main() {
fmt.Println(os.Args[0])
}
练习1.2:
echopackage main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
s, sep := "", ""
for index, arg := range os.Args[1:] {
s += sep + strconv.Itoa(index) + " " + arg
sep = "\n"
}
fmt.Println(s)
}
package main
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
)
var i int = 10
func main() {
// ① 通过 Itoa 方法转换
str1 := strconv.Itoa(i)
// ② 通过 Sprintf 方法转换 %d代表Integer
str2 := fmt.Sprintf("%d", i)
// 打印str1
fmt.Println(str1)
// 打印str2
fmt.Println(str2)
}
练习1.3:
strings.Join03 查找重复的行
// map key value
counts := make(map[string]int)
例子运行
dup1
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
)
func main() {
counts := make(map[string]int)
// 测试读取标准输入使用 Ctrl+D 结束输入
input := bufio.NewScanner(os.Stdin)
for input.Scan() {
counts[input.Text()]++
// line := input.Text()
// counts[line] = counts[line]+1
}
for line, n := range counts {
if n > 1 {
fmt.Printf("%d\t%s\n", n, line)
}
}
}
运行示例:
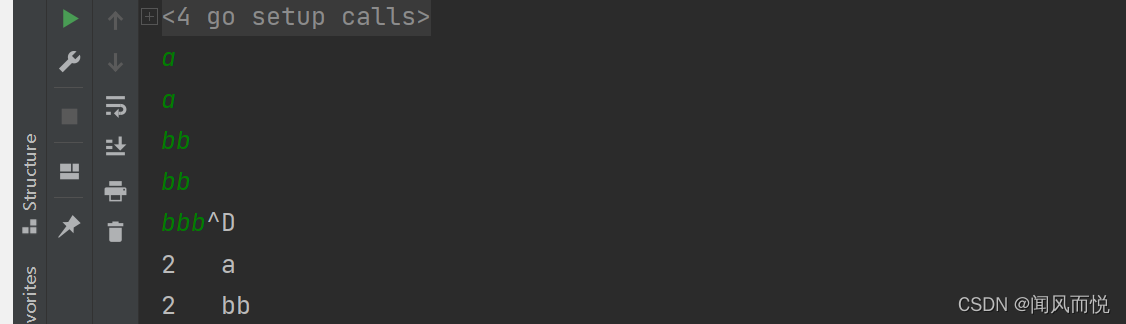
dup2
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
)
// Dup2 prints the count and text of lines that appear more than once
// in the input. It reads from stdin or from a list of named files.
func main() {
counts := make(map[string]int)
files := os.Args[1:]
if len(files) == 0 {
countLines(os.Stdin, counts)
} else {
for _, arg := range files {
f, err := os.Open(arg)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "dup2: %v\n", err)
continue
}
countLines(f, counts)
f.Close()
}
}
for line, n := range counts {
if n > 1 {
fmt.Printf("%d\t%s\n", n ,line)
}
}
}
func countLines(f *os.File, counts map[string]int) {
input := bufio.NewScanner(f)
for input.Scan() {
counts[input.Text()]++
}
// NOTE: ignoring potential errors from input.Err()
}
运行示例:
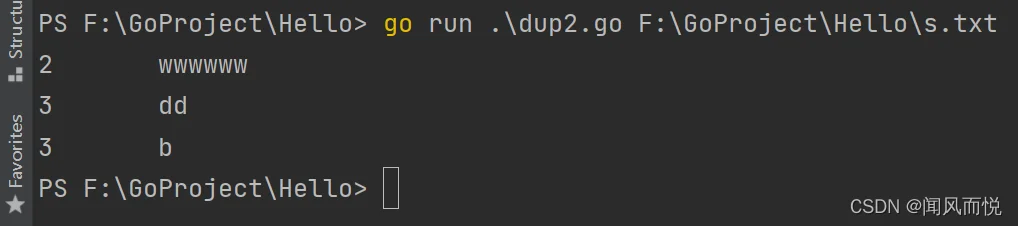
dup3
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"os"
"strings"
)
func main() {
counts := make(map[string]int)
for _, filename := range os.Args[1:] {
data, err := ioutil.ReadFile(filename)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "dup3: %v\n", err)
continue
}
for _, line := range strings.Split(string(data), "\n"){
counts[line]++
}
}
for line, n := range counts {
if n > 1 {
fmt.Printf("%d\t%s\n", n, line)
}
}
}
运行示例:
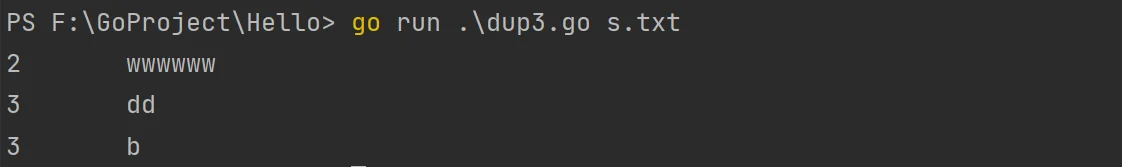
练习
练习1.4:
修改dup2,出现重复的行时打印文件名称
package main
import (
"bufio"
"fmt"
"os"
)
type LnFile struct {
Count int
FileNames []string
}
// Dup2 prints the count and text of lines that appear more than once
// in the input. It reads from stdin or from a list of named files.
func main() {
counts := make(map[string]*LnFile)
files := os.Args[1:]
if len(files) == 0 {
countLine(os.Stdin, counts)
} else {
for _, arg := range files {
f, err := os.Open(arg)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "dup2: %v\n", err)
continue
}
countLine(f, counts)
f.Close()
}
}
for line, n := range counts {
if n.Count > 1 {
fmt.Printf("%d\t%v\t%s\n", n.Count, n.FileNames, line)
}
}
}
func countLine(f *os.File, counts map[string]*LnFile) {
input := bufio.NewScanner(f)
for input.Scan() {
key := input.Text()
_, ok := counts[key]
if ok {
counts[key].Count++
counts[key].FileNames = append(counts[key].FileNames, f.Name())
} else {
counts[key] = new(LnFile)
counts[key].Count = 1
counts[key].FileNames = append(counts[key].FileNames, f.Name())
}
}
// NOTE: ignoring potential errors from input.Err()
}

04 GIF 动画
structpackage main
import (
"bytes"
"image"
"image/color"
"image/gif"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"math"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
// 利萨如图形
var palette = []color.Color{color.White, color.Black}
const (
whiteIndex = 0 // first color in palette
blackIndex = 1 // nexr color in palette
)
func main() {
// The sequence of images is deterministic unless we seed
// the pseudo-random number generator using the current time.
// 图像序列是确定的,除非我们使用当前时间播种伪随机数生成器
rand.Seed(time.Now().UTC().UnixNano())
// 按照书中代码运行编码生成的GIF无法正常打开,改为直接输出字节文件就可以了
// 目测是因为windows环境转了一些控制字符
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
lissajous(buf)
if err := ioutil.WriteFile("output.gif", buf.Bytes(), 0666); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
func lissajous(out io.Writer) {
const (
cycles = 5 // number of complete x oscillator revolutions 完成x振子转数
res = 0.001 // angular resolution 角坐标分辨率
size = 100 // image canvas covers [-size..+size] 图像范围覆盖
nframes = 64 // number of animation frames 动画帧数
delay = 8 // delay between frames in 10ms units 帧间延迟以10ms为单位
)
freq := rand.Float64() * 3.0 // relative frequency of y osillator y振荡器的相对频率
anim := gif.GIF{LoopCount: nframes}
phase := 0.0 // phase diffrence 相位差
for i := 0; i < nframes; i++ {
rect := image.Rect(0, 0, 2*size+1, 2*size+1)
img := image.NewPaletted(rect, palette)
for t := 0.0; t < cycles*2*math.Pi; t += res {
x := math.Sin(t)
y := math.Sin(t*freq + phase)
img.SetColorIndex(size+int(x*size+0.5), size+int(y*size+0.5), blackIndex)
}
phase += 0.1
anim.Delay = append(anim.Delay, delay)
anim.Image = append(anim.Image, img)
}
gif.EncodeAll(out, &anim) // ignoring encoding errors
}
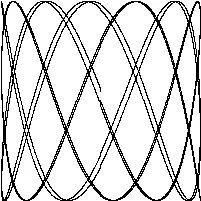
练习
练习1.5:
修改前面的Lissajous程序里的调色板,由黑色改为绿色。我们可以用 color.RGBA{0xRR, 0xGG, 0xBB, 0xff}来得到 #RRGGBB 的色值,三个十六进制的字符串分别代表红、绿、蓝像素
var palette = []color.Color{color.RGBA{ 0, 0, 0, 0xFF}, color.RGBA{ 0, 0xFF, 0, 0xFF}}
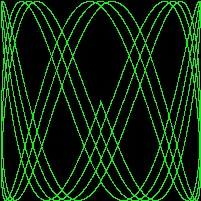
练习1.6:
修改Lissajous程序,修改其调色板来生成更丰富的颜色,然后修改SetColorIndex的第三个参数,看看显示结果吧
package main
import (
"bytes"
"image"
"image/color"
"image/gif"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"math"
"math/rand"
"time"
)
const nColors = 10
func main() {
seed := time.Now()
rand.Seed( seed.Unix() )
var palette []color.Color
for i := 0; i < nColors; i++ {
r := uint8(rand.Uint32() % 256)
g := uint8(rand.Uint32() % 256)
b := uint8(rand.Uint32() % 256)
palette = append( palette, color.RGBA{ r, g, b, 0xFF} )
}
buf := &bytes.Buffer{}
lissajous1(buf, palette)
if err := ioutil.WriteFile("output2.gif", buf.Bytes(), 0666); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
}
func lissajous1(out io.Writer, palette []color.Color) {
const (
cycles = 5
res = 0.001
size = 100
nframes = 64
delay = 8
)
freq := rand.Float64() * 3.0
anim := gif.GIF{LoopCount: nframes}
phase := 0.0
for i := 0; i < nframes; i++ {
rect := image.Rect(0, 0, 2*size+1, 2*size+1)
img := image.NewPaletted(rect, palette)
ncolor := uint8(i % len(palette))
for t := 0.0; t < cycles*2*math.Pi; t += res {
x := math.Sin(t)
y := math.Sin(t*freq + phase)
img.SetColorIndex(size+int(x*size+0.5), size+int(y*size+0.5), ncolor )
}
phase += 0.1
anim.Delay = append(anim.Delay, delay)
anim.Image = append(anim.Image, img)
}
gif.EncodeAll(out, &anim)
}

05 获取URL
http.GetHTTPioutil.ReadAllBodyBody.CloseBodyos.Exitpackage main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
)
func main() {
for _, url := range os.Args[1:] {
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch: %v\n", err)
}
b, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
resp.Body.Close()
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch: reading %s: %v\n", url, err)
os.Exit(1)
}
fmt.Printf("%s", b)
}
}
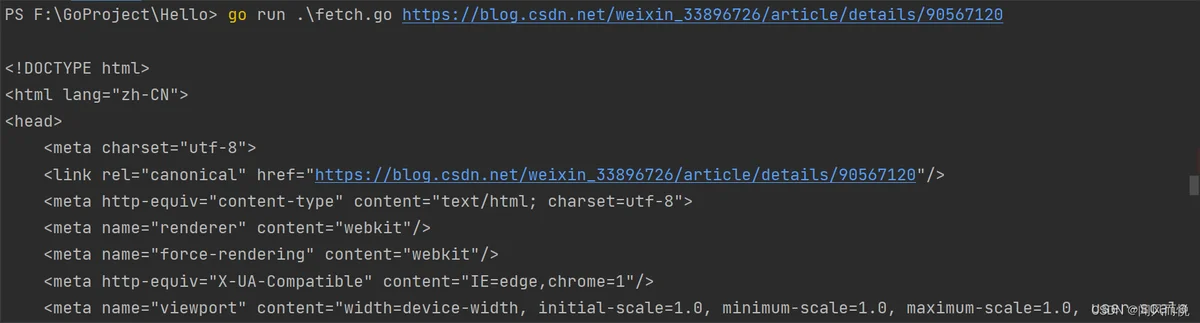
练习
练习1.7:
函数调用io.Copy(dst, src)会从src中读取内容,并将读到的结果写入到dst中,使用这个函数替代例子中的ioutil.ReadAll来拷贝响应结构体到os.Stdout,避免申请一个缓冲区来存储,记得处理io.Copy返回结果中的错误
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"net/http"
"os"
)
func main() {
for _, url := range os.Args[1:] {
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch: %v\n", err)
}
//b, err := ioutil.ReadAll(resp.Body)
// io.Copy(dst Writer, src Reader)
b, err := io.Copy(os.Stdout, resp.Body)
resp.Body.Close()
if err != nil {
//fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch: reading %s: %v\n", url, err)
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch: %v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
fmt.Printf("%s", b)
}
}
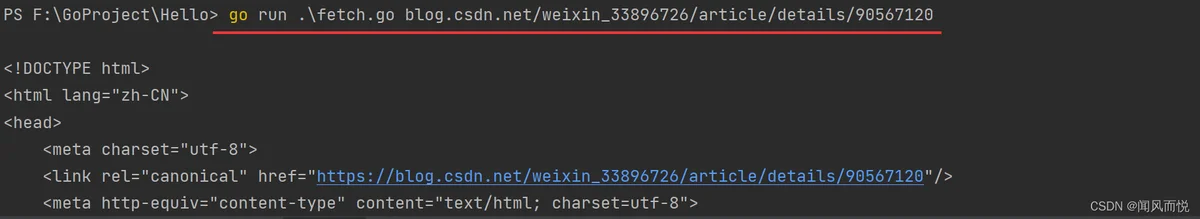
练习1.8:
http://urlstrings.HasPrefixpackage main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"net/http"
"os"
"strings"
)
func main() {
for _, url := range os.Args[1:] {
// strings.HasPrefix
if !strings.HasPrefix(url, "http://") {
url = strings.Join([]string{"http://", url}, "")
}
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch: %v\n", err)
}
// io.Copy(dst Writer, src Reader)
b, err := io.Copy(os.Stdout, resp.Body)
resp.Body.Close()
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch: %v\n", err)
os.Exit(1)
}
fmt.Printf("%s", b)
}
}
练习1.9:
HTTPresp.Statuspackage main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"os"
)
func main() {
for _, url := range os.Args[1:] {
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
fmt.Fprintf(os.Stderr, "fetch: %v\n", err)
}
b := resp.Status
fmt.Printf("%s", b)
}
}

06 并发获取多个URL
goroutinechannelgoroutinemaingoroutinego functiongoroutinegoroutinegoroutinechannelsendreceivegoroutinegoroutinechannelgoroutinechannelch <- expression<-ch// Fetchall fetches URLs in parallel and reports their times and sizes.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
)
func main() {
start := time.Now()
ch := make(chan string)
for _, url := range os.Args[1:] {
go fetch(url, ch) // start a goroutine
}
for range os.Args[1:] {
fmt.Println(<-ch) // receive from channel ch
}
fmt.Printf("%.2fs elapsed\n", time.Since(start).Seconds())
}
func fetch(url string, ch chan<-string) {
start := time.Now()
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
ch <- fmt.Sprint(err) // send to channel ch
return
}
nbytes, err := io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, resp.Body)
if err != nil {
ch <- fmt.Sprintf("while reading %s: %v", url, err)
return
}
secs := time.Since(start).Seconds()
ch <- fmt.Sprintf("%.2fs %7d %s", secs, nbytes, url)
}
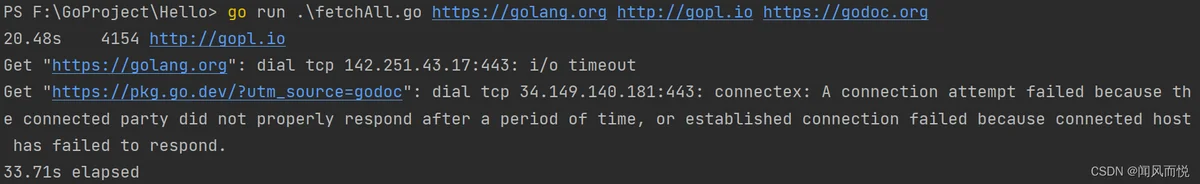
练习
练习1.10:
找一个数据量比较大的网站,用本小节中的程序调研网站的缓存策略,对每个URL执行两遍请求,查看两次时间是否有较大的差别,并且每次获取到的响应内容是否一致,将响应结果输出,以便于进行对比
// Fetchall fetches URLs in parallel and reports their times and sizes.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
)
func main() {
start := time.Now()
ch := make(chan string)
for _, url := range os.Args[1:] {
go fetch(url, ch) // start a goroutine
go fetch(url, ch) // start a goroutine
}
for range os.Args[1:] {
fmt.Println(<-ch) // receive from channel ch
fmt.Println(<-ch) // receive from channel ch
}
fmt.Printf("%.2fs elapsed\n", time.Since(start).Seconds())
}
func fetch(url string, ch chan<-string) {
start := time.Now()
resp, err := http.Get(url)
if err != nil {
ch <- fmt.Sprint(err) // send to channel ch
return
}
nbytes, err := io.Copy(ioutil.Discard, resp.Body)
if err != nil {
ch <- fmt.Sprintf("while reading %s: %v", url, err)
return
}
secs := time.Since(start).Seconds()
ch <- fmt.Sprintf("%.2fs %7d %s", secs, nbytes, url)
}
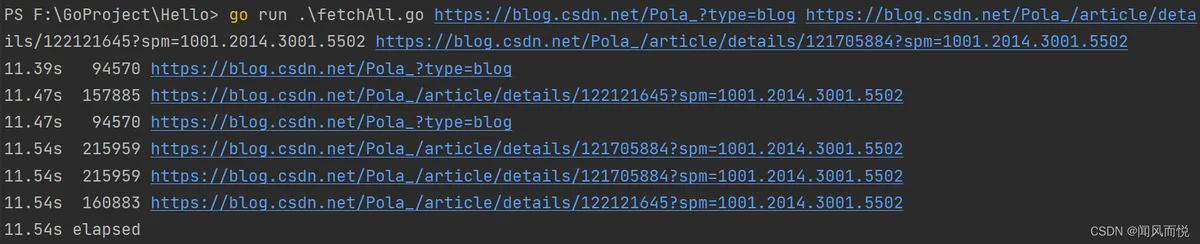
练习1.11:
在fetchall中尝试使用长一些的参数列表,比如使用在alexa.com的上百万网站里排名靠前的,如果一个网站没有回应,程序将采取怎样的行为?
07 Web服务
main/handler/8000http.Requestserver1
// Server1 is a minimal "echo" server.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", handler) // each request calls handler
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8000", nil))
}
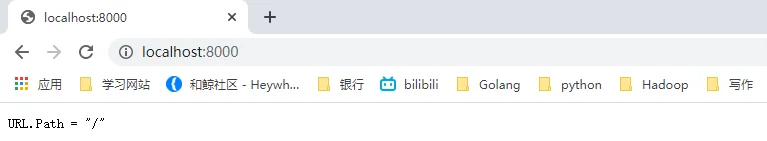
// handler echoes the Path component of the request URL r.
func handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "URL.Path = %q\n", r.URL.Path)
}
server2
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
"sync"
)
var mu sync.Mutex
var count int
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", Handler)
http.HandleFunc("/count", counter)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8001", nil))
}
// handler echoes the Path component of the requested URL
func Handler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 上锁
mu.Lock()
// 避免同一时刻两个请求去更新count
count++
// 保证每次修改变量的最多只有一个goroutine
mu.Unlock()
fmt.Fprintf(w, "URL.Path = %q\n", r.URL.Path)
}
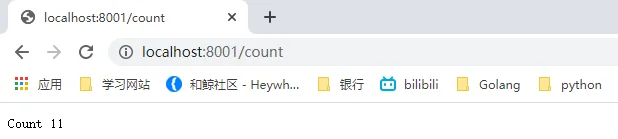
// counter echoes the number of calls so far
func counter(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
mu.Lock()
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Count %d\n", count)
mu.Unlock()
}
server3
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/", HandLer)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8001", nil))
}
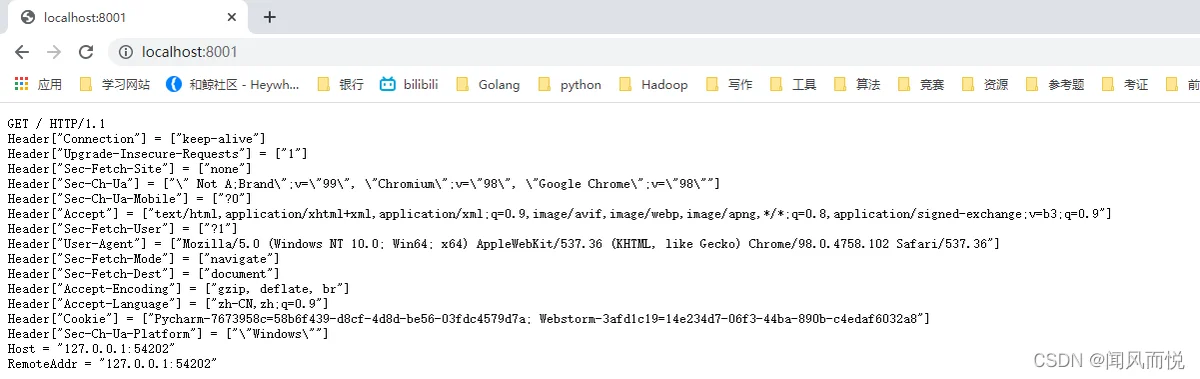
func HandLer(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "%s %s %s\n", r.Method, r.URL, r.Proto)
for k, v := range r.Header {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Header[%q] = %q\n", k, v)
}
// %q 带双引号的字符串"abc" 或 带单引号的 rune 'c'
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Host = %q\n", r.RemoteAddr)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "RemoteAddr = %q\n", r.RemoteAddr)
if err := r.ParseForm(); err != nil {
log.Print(err)
}
for k, v := range r.Form {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Form[%q] = %q\n", k, v)
}
}
练习
练习1.12:
修改Lissajour服务,从URL读取变量,比如你可以访问http://localhost:8000/?cycles=20 这个URL,这样访问可以将程序里的cycles默认的5修改为20。字符串转换为数字可以调用strconv.Atoi函数。你可以在godoc里查看strconv.Atoi的详细说明
package main
import (
"image"
"image/color"
"image/gif"
"io"
"log"
"math"
"math/rand"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"time"
)
var palette = []color.Color{color.White, color.Black}
const (
whiteIndex = 0
blackIndex = 1
)
type lconfig struct {
cycles float64
res float64
freq float64
size int
frames int
delay int
}
func main() {
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
lconf := lconfig{
cycles: 5,
res: 0.001,
freq: rand.Float64() * 3.0,
size: 100,
frames: 64,
delay: 8,
}
http.HandleFunc("/", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
confs := r.URL.Query()
for i, c := range confs {
switch i {
case "cycles":
lconf.cycles, _ = strconv.ParseFloat(c[0], 64)
case "freq":
lconf.freq, _ = strconv.ParseFloat(c[0], 64)
case "res":
lconf.res, _ = strconv.ParseFloat(c[0], 64)
case "size":
lconf.size, _ = strconv.Atoi(c[0])
case "frames":
lconf.frames, _ = strconv.Atoi(c[0])
case "delay":
lconf.delay, _ = strconv.Atoi(c[0])
}
}
lissajous(w, lconf)
})
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("localhost:8000", nil))
return
}
func lissajous(out io.Writer, set lconfig) {
anim := gif.GIF{LoopCount: set.frames}
phase := 0.0 // phase difference
for i := 0; i < set.frames; i++ {
rect := image.Rect(0, 0, 2*set.size+1, 2*set.size+1)
img := image.NewPaletted(rect, palette)
for t := 0.0; t < set.cycles*2*math.Pi; t += set.res {
x := math.Sin(t)
y := math.Sin(t*set.freq + phase)
img.SetColorIndex(set.size+int(x*float64(set.size)+0.5), set.size+int(y*float64(set.size)+0.5), blackIndex)
}
phase += 0.1
anim.Delay = append(anim.Delay, set.delay)
anim.Image = append(anim.Image, img)
}
gif.EncodeAll(out, &anim)
}
08 本章要点
控制流
switch coinflip() {
case "heads":
heads++
case "tails":
tails++
default:
fmt.Println("landed on edge!")
}
switch {
case x > 0 :
return +1
default:
return 0
}
命名类型
type Point struct {
X, Y int
}
指针
&*方法和接口
方法可以被关联到任意一种命名类型包(packages)
-
Go 语言里有一些很好用的package,并且这些package是可以扩展的
-
在写一个新程序之前可以先去检查一下是否存在现成的库可以帮助你更高效地完成这件事情
注释
/* ... *//////*