1. 链表
顺序表连续的链表(Linked list)节点单向链表(Singly linked list)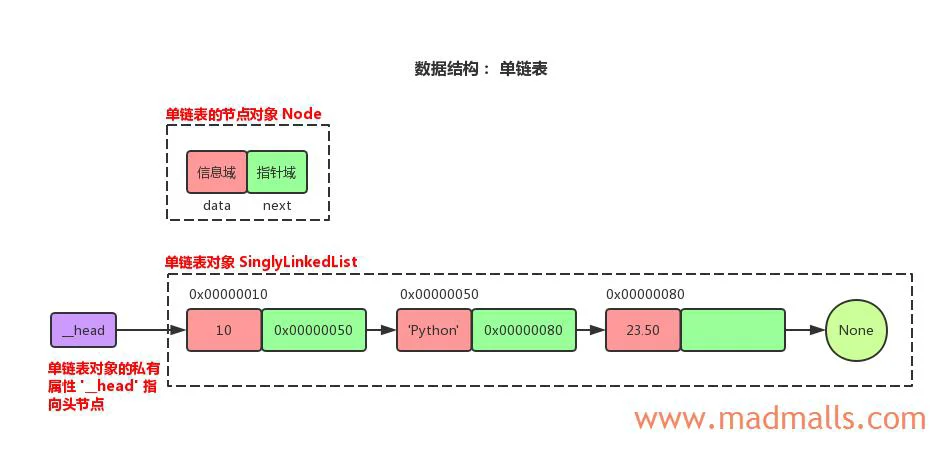
单向链表只可向一个方向遍历,一般查找一个节点的时候需要从第一个节点开始每次访问下一个节点,一直访问到需要的位置
2.1 Python实现
接下来我们使用Python 3来构建单链表数据结构,首先需要定义一个节点类:
class Node:
'''单链表的节点'''
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value # 节点的信息域
self.next = None # 节点的指针域
def __repr__(self):
return 'Node({!r})'.format(self.value)
然后定义单链表类:
class SinglyLinkedList:
def __init__(self, node=None):
'''创建一个单链表对象时,如果不传入头节点,则创建空链表'''
self.__head = node
(1) 判断是否空链表
__headdef is_empty(self):
'''判断是否为空链表'''
return self.__head is None
(2) 求链表的长度
curcur = self.__headcountcurcur.next == Nonecurcountdef length(self):
'''求链表的长度'''
cur = self.__head # 游标,用来表示当前节点
count = 0 # 用来统计已遍历的节点数目
# 1. 如果是空链表,self.__head为None,则cur为None,不会进入循环体,最后返回 count = 0,符合
# 2. 如果不是空链表,当cur移动到尾节点时,cur.next 是None,循环体中的 cur = cur.next 会让 cur = None,继续往后移动时会退出循环
while cur is not None:
count += 1
cur = cur.next # 向后移动游标
return count
(3) 遍历链表
逻辑跟求长度一样,注意,这里使用生成器语法,将每个节点的值产出供客户代码使用
